#Inflammatory_Breast_Cancer #Aggressive #Swelling #Spreasd_Quickly #more_common_African_American_women #Also_Affect_men #Redness_breast #Swelling_breast #Warmth #Orange-peel_appearance #Flattening_nipple

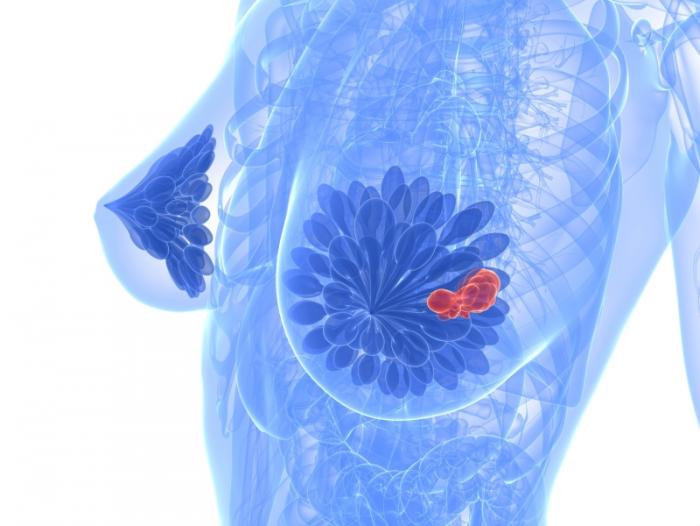
Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is a rare and aggressive form of breast cancer. According to the American Cancer Society, about 1% of all breast cancer cases in the United States are inflammatory breast cancers.
Inflammatory breast cancer usually starts with the reddening and swelling of the breast instead of a distinct lump. IBC tends to grow and spread quickly, with symptoms worsening within days or even hours. It’s important to recognize symptoms and seek prompt treatment. Although inflammatory breast cancer is a serious diagnosis, keep in mind that treatments today are better at controlling the disease than they used to be.
The average age at diagnosis of inflammatory breast cancer in the United States is 57 for white women and 52 for African American women. These ages are about 5 years younger than the average ages at diagnosis for other forms of breast cancer. According to the American Cancer Society, inflammatory breast cancer is more common in African American women. A 2008 study found that being overweight makes a person more likely to develop IBC. Like other forms of breast cancer, IBC can also affect men.
Common symptoms of IBC include:
Redness of the breast: Redness involving part or all of the breast is a hallmark of inflammatory breast cancer. Sometimes the redness comes and goes.
Swelling of the breast: Part of or all of the breast may be swollen, enlarged, and hard.
Warmth: The breast may feel warm.
Orange-peel appearance: Your breast may swell and start to look like the peel of a navel orange (this is called “peau d’orange”).
Other skin changes: The skin of the breast might look pink or bruised, or you may have what looks like ridges, welts, or hives on your breast.
Swelling of lymph nodes: The lymph nodes under your arm or above the collarbone may be swollen.
Flattening or inversion of the nipple: The nipple may go flat or turn inward.
Aching or burning: Your breast may ache or feel tender.

Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is a rare and aggressive form of breast cancer. According to the American Cancer Society, about 1% of all breast cancer cases in the United States are inflammatory breast cancers.
Inflammatory breast cancer usually starts with the reddening and swelling of the breast instead of a distinct lump. IBC tends to grow and spread quickly, with symptoms worsening within days or even hours. It’s important to recognize symptoms and seek prompt treatment. Although inflammatory breast cancer is a serious diagnosis, keep in mind that treatments today are better at controlling the disease than they used to be.
The average age at diagnosis of inflammatory breast cancer in the United States is 57 for white women and 52 for African American women. These ages are about 5 years younger than the average ages at diagnosis for other forms of breast cancer. According to the American Cancer Society, inflammatory breast cancer is more common in African American women. A 2008 study found that being overweight makes a person more likely to develop IBC. Like other forms of breast cancer, IBC can also affect men.
Common symptoms of IBC include:
Redness of the breast: Redness involving part or all of the breast is a hallmark of inflammatory breast cancer. Sometimes the redness comes and goes.
Swelling of the breast: Part of or all of the breast may be swollen, enlarged, and hard.
Warmth: The breast may feel warm.
Orange-peel appearance: Your breast may swell and start to look like the peel of a navel orange (this is called “peau d’orange”).
Other skin changes: The skin of the breast might look pink or bruised, or you may have what looks like ridges, welts, or hives on your breast.
Swelling of lymph nodes: The lymph nodes under your arm or above the collarbone may be swollen.
Flattening or inversion of the nipple: The nipple may go flat or turn inward.
Aching or burning: Your breast may ache or feel tender.







 because it hasn’t spread beyond the milk duct into any normal surrounding breast tissue. DCIS isn’t life-threatening, but having DCIS can increase the risk of developing an invasive breast cancer later on.
because it hasn’t spread beyond the milk duct into any normal surrounding breast tissue. DCIS isn’t life-threatening, but having DCIS can increase the risk of developing an invasive breast cancer later on.